How to Create and Maintain a Financial Budget: Intermediate Guide

Introduction to Advanced Strategies:
In this intermediate guide on how to create and maintain a financial budget, we will explore more detailed and personalized strategies for your financial planning. Effectively managing your finances is essential to achieving greater goals, such as investments, financial stability, and preparing for unexpected events. As you transition from the basics to more complex strategies, it is crucial to adapt your budget to different scenarios and optimize your resources. Throughout this article, you will discover how a well-structured budget can transform your financial life, providing the security and freedom to achieve your dreams.
Benefits of Advancing in Financial Control
Advancing in financial control brings a range of benefits that go beyond merely organizing personal finances. Firstly, it helps with monthly investments, allowing you to build a diversified and secure portfolio. Additionally, being financially prepared for life changes, such as buying a house or welcoming a child, becomes more possible. Another significant benefit is the increased savings for long-term goals, such as retirement or dream vacations. Lastly, enhanced financial control improves your bargaining skills, whether to secure better interest rates or obtain more favorable payment terms.

The image illustrates the key benefits of financial control in a visual and organized manner, divided into four numbered sections.
Advanced Strategies to Create and Maintain a Budget
To create and maintain an effective financial budget, it is essential to adopt more detailed strategies that go beyond the basics:
Identify consumption patterns: Analyze your ongoing expenses and find areas where there may be waste. This will allow you to adjust your spending according to your financial priorities.
Example: “After analyzing his monthly expenses, João realized he was spending $ 500 per month on dining out. By replacing part of these expenses with home-cooked meals, he saved $ 300 monthly, which was directed to his emergency fund.”

On the left side, a sophisticated meal with a highlighted receipt indicates a high cost of $500+, symbolizing restaurant consumption. On the right side, a well-lit home kitchen features a glass jar filled with money and a pink piggy bank beside it, representing the $200 saved by choosing to prepare meals at home. The composition conveys the message that simple adjustments in spending habits can lead to significant savings.
Include One-time expenses: Plan for costs such as annual taxes, school tuition, or car maintenance. This way, you can avoid unpleasant surprises.

The image shows a woman reviewing financial documents, planning for one-time expenses. A piggy bank and car symbolize saving for annual costs like taxes and vehicle expenses.
How to Plan for One-Time Expenses
Integrate short, medium, and long-term goals: Direct your budget toward specific objectives, such as paying off debts (short-term), building an emergency fund (medium-term), or saving for retirement (long-term).
Example: “Carlos set three financial goals: pay off a $ 2,000 debt in 6 months, save $ 10,000 in 2 years for a trip, and invest for retirement. He allocated $ 500 per month for the debt, $ 400 for the trip, and $ 300 for an investment fund, balancing his priorities.”

The image shows a man with a planner, outlining goals: paying debts, building an emergency fund, and saving for retirement, with symbols of money and time management.
Distribute your budget in detail: Assign resources to specific categories, such as leisure, education, and healthcare, maintaining a healthy balance between needs and wants.
Example: “With a net salary of $ 5,000, Júlia organized her budget as follows:”
50% for necessities ($ 2,500: rent, bills, transportation, food);
20% para lazer ($ 1.000: academia, cinema, viagens)
30% para metas financeiras (
$ 1.500: investimentos e fundo de emergência).”
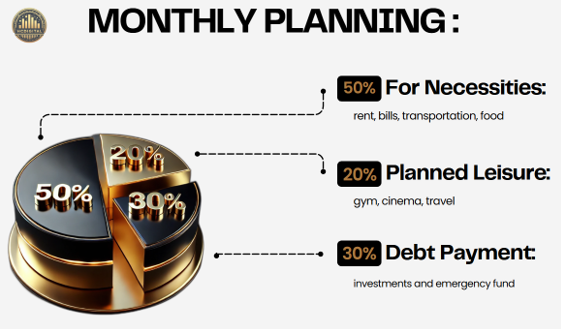
The image shows a pie chart illustrating the budget: 50% for necessities, 20% for leisure, and 30% for financial goals like investments and an emergency fund.
Tools and Techniques for Advanced Financial Control
Utilizar ferramentas adequadas pode transformar a maneira como você gerencia suas finanças. Aqui estão algumas sugestões:
Mint: One of the most popular apps in the United States, Mint connects your bank accounts, credit cards, and loans to provide a complete overview of your finances. It automatically categorizes your expenses, helps create personalized budgets, and sends alerts about payments and overspending.
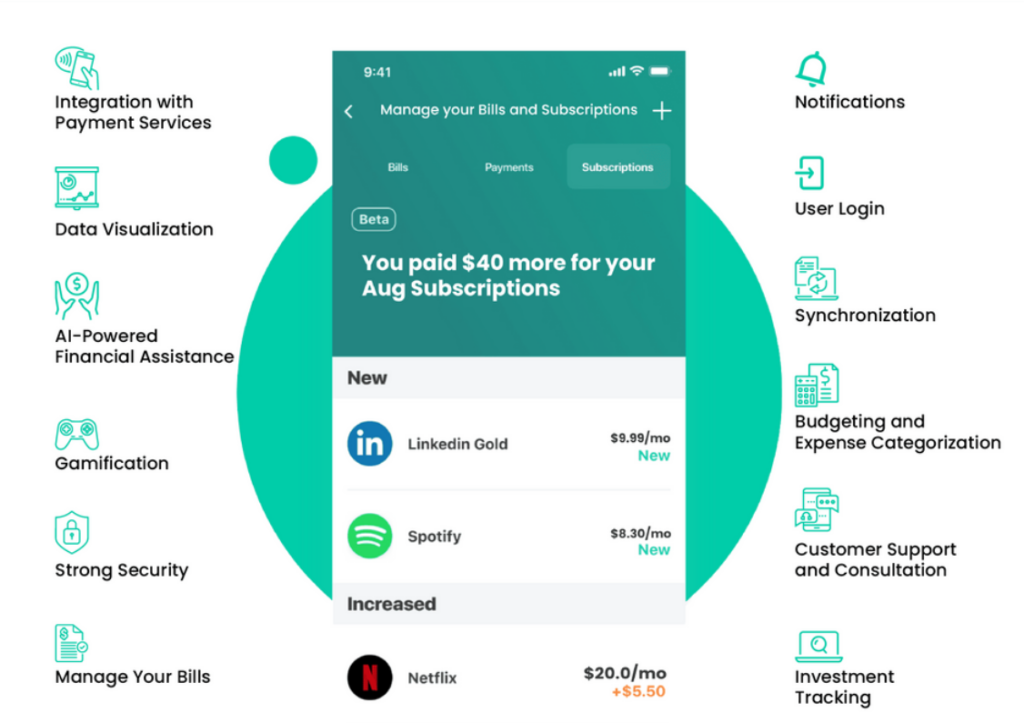
YNAB (You Need A Budget): Ideal for those who want to take a proactive approach to financial control, YNAB encourages users to assign a specific purpose to every dollar they earn. With a strong focus on financial education, the tool helps build solid habits and achieve financial goals.
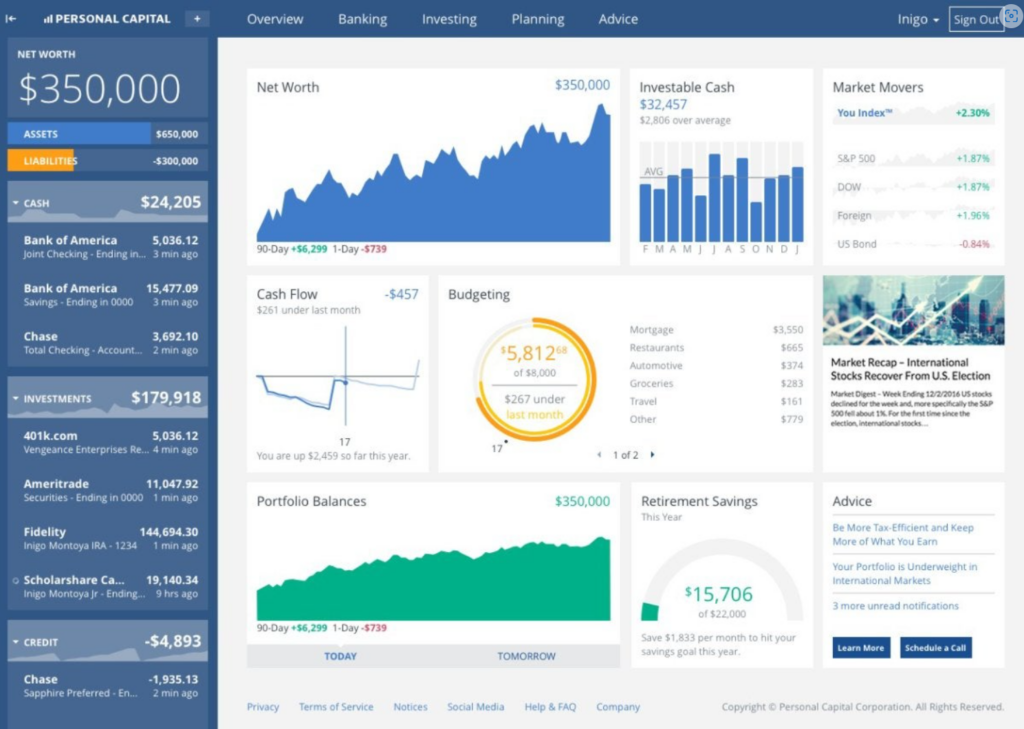
Personal Capital: A platform that combines budgeting and investment management. In addition to tracking expenses and income, it offers robust tools to monitor portfolios and calculate net worth, making it ideal for those seeking financial control and long-term planning.
EveryDollar: Developed by Dave Ramsey’s team, this app uses the zero-based budgeting method. It helps you plan and allocate every dollar in a practical and efficient way. The simple interface is perfect for those who are just starting to organize their finances.
Tiller Money: An innovative solution for those who prefer customized spreadsheets. It connects to your bank accounts and automatically updates your financial data in Google Sheets or Excel. It is ideal for individuals seeking full control over their budget structure.

Goodbudget: Based on the envelope system, Goodbudget allows you to plan and manage your expenses by dividing your income into specific categories. It is especially useful for families or couples who want to share financial information.
PocketGuard: This app helps simplify your finances by connecting to your bank accounts and showing how much money you can safely spend after covering all fixed expenses and financial goals. It also automatically categorizes your expenses.
Additionally, financial automation can simplify the control process by allowing you to schedule automatic payments and transfers, ensuring that your bills are paid on time and your savings goals are achieved without extra effort.
How to Review and Adjust Your Budget Monthly
Reviewing and adjusting your budget monthly is an essential practice for maintaining effective financial control.
Analyze monthly reports: Examine your income and expenses to Identify patterns or unnecessary expenses.
Identify areas of overspending: Determine where you can cut back without compromising your essential needs.
Compare monthly results: Assess whether you are achieving your financial goals and adjust as needed.
Example: “In one month, Pedro received a higher electricity bill due to extreme heat. He adjusted his budget by reducing leisure expenses to cover the difference, keeping his financial goals intact.”

The image depicts the process of reviewing and adjusting the monthly budget, as described in the example. An open notebook displays organized notes with the categories “Expenses,” “Savings,” and “Adjustments,” highlighting the detailed financial analysis. Next to it, a calculator and a stack of money symbolize practical control and resource management. On the laptop screen, visual charts of expenses and income represent the evaluation of monthly reports and the identification of patterns or excesses. The scene connects to Pedro’s example, where he adjusted his leisure expenses after an unexpected bill, keeping his financial goals intact. The organized environment reinforces the importance of regularly reviewing and balancing financial priorities.
This regular review ensures that your budget is always aligned with your goals and needs.
Intermediate Examples
Planning to Buy a Property: Determine how much you can save monthly and adjust your budget to maximize this savings. Remember to include additional costs such as taxes and future maintenance.
Example: “Mariana saved $ 1,500 per month for 3 years, reaching a total of $ 54,000 for the down payment on her apartment. She also set aside $ 200 monthly to cover additional costs, such as deed registration and moving expenses.”

The image illustrates financial planning for purchasing a property, connecting to the example mentioned. A jar labeled “Home Fund” is prominently featured, containing money set aside for the goal, while an open notebook displays detailed calculations and notes on monthly savings and additional costs, such as taxes and maintenance. In the background, a laptop presents financial progress charts, and a miniature house reinforces Mariana’s goal, who saved $ 1,500 per month to reach the down payment target for her apartment, maintaining an organized and effective plan.
Simulation of Cuts in Variable Expenses: Reduce expenses such as dining out or non-essential subscriptions. Redirect these savings to strengthen your emergency fund or accelerate debt repayment.
Example: “After identifying that she was spending $ 400 per month on entertainment, Laura decided to reduce it to $ 200, redirecting the remaining $ 200 to pay off a high-interest debt.”

The image represents financial planning focused on reducing variable expenses, as described in the text. A notebook details categories such as entertainment and subscriptions, indicating adjustments in amounts. A piggy bank symbolizes the redirection of savings toward financial priorities, such as the emergency fund. On the laptop, graphs display a comparison between reduced expenses and achieved goals, connecting to Laura’s example, who saved $ 200 on entertainment to accelerate debt repayment. The composition reflects an organized and strategic financial management process.
Practical Tips to Maintain an Intermediate-Level Budget
Maintaining an intermediate-level budget requires discipline and adaptation:
Adapt to changes in income: Adjust your budget for salary increases or periods of lower earnings, ensuring that your finances remain balanced.
Adapt to changes in income: Adjust your budget for salary increases or periods of lower earnings, ensuring that your finances remain balanced.
Conduct quarterly or annual reviews: Evaluate your progress and adjust goals as needed.
Track personal financial indicators: Monitor your savings rate and debt-to-income ratio to maintain a clear view of your financial health.
Take the First Step Toward Financial Freedom
Advancing in financial control is a crucial step toward achieving stability and freedom. Continuously testing and adjusting your strategies ensures that you are always aligned with your goals.
Did you enjoy this article? Leave your comment below sharing your experiences or questions about financial control. Feel free to explore other content and discover more practical tips to transform your financial life. And, of course, don’t forget to share this article with friends and family who may also benefit from these strategies. Let’s work together to build a stronger financial future!



